- Standards amino acid were from Merck
- PITC, trifluoroacetic acid and triethylamine (sequanal grade) were from Fluka
- acetonitrile (HPLC grade) was from Pierce
Derivatization of individual amino acids with PITC
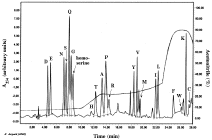
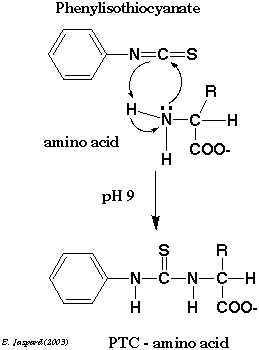
PITC reacts with primary and secondary amines, leading to PTC-amino acids detectable at 254 nm (see figure below).
This method is sensitive down to at least 10 pmol (Bergman et al.).
- standard amino acids plus homoserine (30 to 100 Ámol) were first neutralized with 1 mL ethanol:water:TEA (2:2:1, v/v) and evaporated under vacuum
- samples were then derivatized by addition of 500 ÁL ethanol:water:TEA:PITC (7:1:1:1, v/v) corresponding to 5 times PITC excess (mol/mol)
- samples were incubated for 30 min at room temperature and evaporated under vacuum
- PTC-amino acids were dissolved in ethanol:water (at various ratio depending on the hydrophobic nature of the PTC-amino acid) and stored at - 20°C
Reference : Bergman, T., Carlquist, M., and Jörnvall, H. (1986) in Advanced Methods in Protein Microsequence Analysis (Wittmann - Liebold, B., Salnikov, J., and Erdmann, V. A., Eds.) 45 - 55, Berlin/Heidelberg